| 基于跨模态空间匹配的多模态肺部肿块分割网络 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 李家忻, 陈后金, 彭亚辉, 李艳凤. 基于跨模态空间匹配的多模态肺部肿块分割网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 11-17. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210710 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 李家忻 陈后金 彭亚辉 李艳凤 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 北京交通大学电子信息工程学院 北京 100044 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金 (62172029% 61872030% 61771039) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 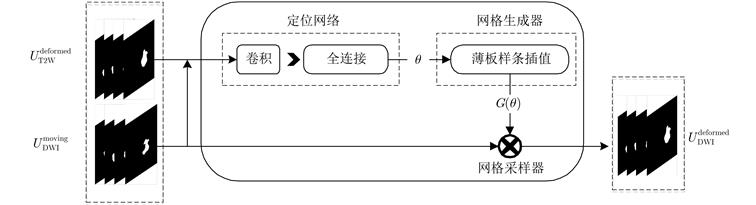
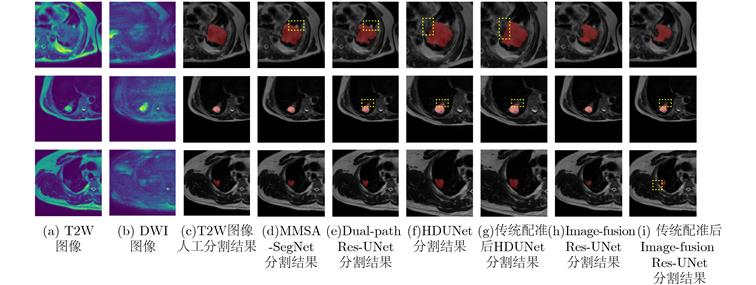
现有多模态分割方法通常先对图像进行配准,再对配准后的图像进行分割。对于成像特点差异较大的不同模态,两阶段的结构匹配与分割算法下的分割精度较低。针对该问题,该文提出一种基于跨模态空间匹配的多模态肺部肿块分割网络(MMSASegNet),其具有模型复杂度低和分割精度高的特点。该模型采用双路残差U型分割网络作为骨干分割网络,以充分提取不同模态输入特征,利用可学习的空间变换网络对其输出的多模态分割掩膜进行空间结构匹配;为实现空间匹配后的多模态特征图融合,形变掩膜和参考掩膜分别与各自模态相同分辨率的特征图进行矩阵相乘,并经特征融合模块,最终实现多模态肺部肿块分割。为提高端到端多模态分割网络的分割性能,采用深度监督学习策略,联合损失函数约束肿块分割、肿块空间匹配和特征融合模块,同时采用多阶段训练以提高不同功能模块的训练效率。实验数据采用T2权重(T2W)磁共振图像和扩散权重磁共振图像(DWI)肺部肿块分割数据集,该方法与其他多模态分割网络相比,DSC (Dice Similarity Coefficient)和HD (Hausdorff Distance)等评价指标均显著提高。
|
| 关 键 词: | 肺部肿块分割 多模态磁共振成像 空间变换网络 联合训练 深度监督 |
| 收稿时间: | 2021-07-15 |
| 修稿时间: | 2021-10-20 |
| 本文献已被 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《电子与信息学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《电子与信息学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|


