Redeposition in CO2 textile dry cleaning |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Environmental Engineering, Zhejiang University, 866 Yuhangtang Road, Hangzhou 310058, PR China;2. Zhejiang Provincial Engineering Research Center of Industrial Boiler & Furnace Flue Gas Pollution Control, 866 Yuhangtang Road, Hangzhou 310058, PR China;1. Graduate School of Medicine and Engineering, University of Yamanashi, Kofu 400-8511, Yamanashi, Japan;2. Graduate School of Engineering, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8601, Japan |
| |
| Abstract: | 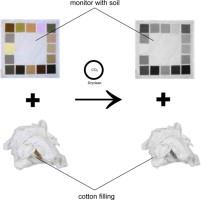
Perchloroethylene (PER) is commonly used as cleaning solvent in the textile dry-cleaning industry but this chemical is toxic by nature. One of the potential PER replacements is carbon dioxide (CO2), which is non-toxic, cheap, and widely available. Previous studies have indicated that the particulate soil removal with CO2 is lower compared to that of PER. While the particulate soil removal of the CO2 dry-cleaning was studied, it was found that redeposition of particulate soil occurs. Several experiments have been carried out to study and reduce this problem. In these experiments, textiles stained with different kinds of particulate soils were cleaned using a 25 L CO2 dry-cleaning set-up. It was found that the redeposition level increases along with washing time, while rinsing has little influence. Modifying the filtration system by using scavenger textile, or adding a cellulose compound to the cleaning vessel as anti redeposition agent can significantly reduce redeposition. |
| |
| Keywords: | Dry cleaning Carbon dioxide Redeposition |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

