| 基于微电流刺激的多强度分级虚拟触觉反馈 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 谭铭昱, 花浩镪, 熊奇炜, 朱齐, 舒琳, 徐向民, 梁家铭, 魏磊, 黄国志, 曾庆. 基于微电流刺激的多强度分级虚拟触觉反馈[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2023, 60(9): 2015-2027. DOI: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.202330420 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 谭铭昱 花浩镪 熊奇炜 朱齐 舒琳 徐向民 梁家铭 魏磊 黄国志 曾庆 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.华南理工大学未来技术学院 广州 511442;2.华南理工大学电子与信息学院 广州 510641;3.琶洲实验室 广州 510335;4.腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司RoboticsX实验室 广东深圳 518054;5.迪肯大学 澳大利亚墨尔本 3220;6.南方医科大学珠江医院康复医学科 广州 510280;7.南方医科大学康复医学院 广州 510515 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家重点研发计划(2022YFB4500600);;中山市科技计划(2019AG024); |
| |
| 摘 要: | 
触觉反馈可以有效提高用户的虚拟现实交互的沉浸感,但是采用振动方式的触觉反馈存在反馈模态单一的缺陷;采用机械传动式、微流驱动方式的触觉反馈存在结构复杂、难以集成等缺陷. 微电流触觉反馈具有集成度高、反馈模态丰富等优点,但是存在反馈强度识别准确率不够和长时间作用下易造成不适感等问题. 为了解决这些问题,设计了基于微电流刺激的新型多强度电触觉反馈系统,通过研究电流参数、电极阵列和接地电极等影响因素,并引入双相电流脉冲,优化电流正负电荷量比值等方式,确定了该系统的刺激模式.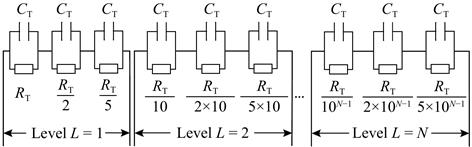
35名受试者的心理物理学实验结果表明该反馈系统能够在有效减少微电流刺激带来不适的同时实现93.3%和81.7%的四级和五级强度识别准确率,优于传统方法,这可能是具有广泛应用场景的触觉反馈设备.
|
| 关 键 词: | 触觉反馈 微电流刺激 优化的电刺激范式 高准确率 |
| 收稿时间: | 2023-05-31 |
| 修稿时间: | 2023-07-24 |
|
| 点击此处可从《计算机研究与发展》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《计算机研究与发展》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



