| 基于边缘辅助极线Transformer的多视角场景重建 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 童伟, 张苗苗, 李东方, 吴奇, 宋爱国. 基于边缘辅助极线Transformer的多视角场景重建[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(10): 3483-3491. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221244 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 童伟 张苗苗 李东方 吴奇 宋爱国 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.南京理工大学机械工程学院 南京 210094;2.上海交通大学电子信息与电气工程学院 上海 200240;3.福州大学电气工程与自动化学院 福州 350108;4.东南大学仪器科学与工程学院 南京 210096 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金 (U1933125, 62171274),国家自然科学基金“叶企孙”重点项目(U2241228),国防创新特区项目 (193-CXCY-A04-01-11-03,223-CXCY-A04-05-09-01),上海市级科技重大专项 (2021SHZDZX) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 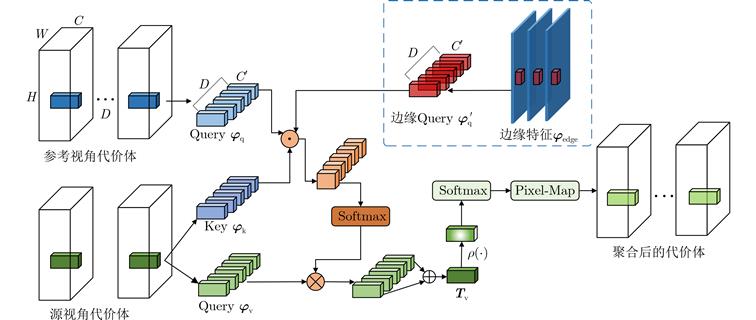
基于深度学习的多视角立体几何(MVS)旨在通过多个视图重建出稠密的3维场景。然而现有的方法通常设计复杂的2D网络模块来学习代价体聚合的跨视角可见性,忽略了跨视角2维上下文特征在3D深度方向的一致性假设。此外,基于多阶段的深度推断方法仍需要较高的深度采样率,并且在静态或预先设定的范围内采样深度值,容易在物体边界以及光照遮挡等区域产生错误的深度推断。为了缓解这些问题,该文提出一种基于边缘辅助极线Transformer的密集深度推断模型。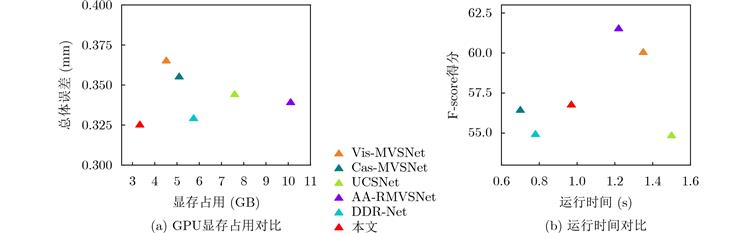
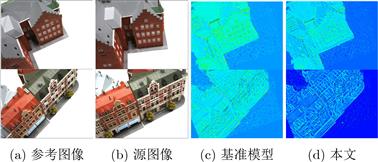
与现有工作相比,具体改进如下:将深度回归转换为多深度值分类进行求解,在有限的深度采样率和GPU占用下保证了推断精度;设计一种极线Transformer模块提高跨视角代价体聚合的可靠性,并引入边缘检测分支约束边缘特征在极线方向的一致性;为了提高弱纹理区域的精度,设计了基于概率成本体积的动态深度范围采样机制。与主流的方法在公开的数据集上进行了综合对比,实验结果表明所提模型能够在有限的显存占用下重建出稠密准确的3D场景。特别地,相比于Cas-MVSNet,所提模型的显存占用降低了35%,深度采样率降低约50%,DTU数据集的综合误差从0.355降低至0.325。
|
| 关 键 词: | 多视角场景重建 多视角立体几何 深度估计 极线几何 Transformer |
| 收稿时间: | 2022-09-26 |
| 修稿时间: | 2022-11-28 |
|
| 点击此处可从《电子与信息学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《电子与信息学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



