Dry sliding wear of epoxy/cenosphere syntactic foams |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Mechanical Engineering, BVB College of Engineering and Technology, Hubli, Karnataka, India;2. Lightweight Materials Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Institute of Technology Karnataka, Surathkal, India;3. Department of Industrial Production and Automobile Engineering, BVB College of Engineering and Technology, Hubli, Karnataka, India;4. Department of Materials Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India;5. Composite Materials and Mechanics Laboratory, Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Department, Polytechnic School of Engineering, New York University, Brooklyn, NY 11201, USA;6. Department of Automobile Engineering, BVB College of Engineering and Technology, Hubli, Karnataka, India;1. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, 208016, India;2. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi, 110016, India;1. Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia;2. Institute of Technology, Middle Technical University, 29008 Alzafaranya, Baghdad, Iraq;3. Laboratory of Biocomposite Technology, Institute of Tropical Forestry and Forest Products (INTROP), Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia;4. Department of Mechanical and Materials, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600 Bangi, Malaysia;5. Department of Aerospace Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia;1. Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Bertalan Lajos utca 7., Budapest 1111, Hungary;2. MTA–BME Research Group for Composite Science and Technology, Műegyetem rakpart 3., Budapest 1111, Hungary;1. Department of Mechanical Engineering, National University of Singapore, 9 Engineering Drive 1, Singapore, 117576, Singapore;2. Lightweight Materials Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Institute of Technology Karnataka, Surathkal, India |
| |
| Abstract: | 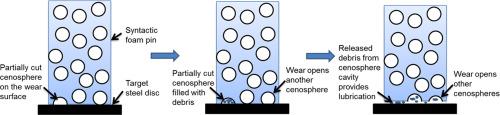
Dry sliding wear behavior of epoxy matrix syntactic foams filled with 20, 40 and 60 wt% fly ash cenosphere is reported based on response surface methodology. Empirical models are constructed and validated based on analysis of variance. Results show that syntactic foams have higher wear resistance than the matrix resin. Among the parameters studied, the applied normal load (F) had a prominent effect on wear rate, specific wear rate (ws) and coefficient of friction (μ). With increasing F, the wear rate increased, whereas ws and μ decreased. With increase in filler content, the wear rate and ws decreased, while the μ increased. With increase in sliding velocity as well as sliding distance, the wear rate and ws show decreasing trends. Microscopy revealed broken cenospheres forming debris and extensive deformation marks on the wear surface. |
| |
| Keywords: | Cenosphere Wear Syntactic foam Response surface methodology |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

