| 表面微结构金属干式电极制造及细菌粘附性能研究 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 刘韶宇, 周伟, 李瑶瑶, 等. 表面微结构金属干式电极制造及细菌粘附性能研究[J]. 光电工程, 2017, 44(12): 1187-1193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.12.006 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 刘韶宇 周伟 李瑶瑶 方家畅 张陈应 陆荣华 叶桂峰 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1. 厦门大学机电工程系,福建 厦门 361005; 2. 江南大学包装工程系,江苏 无锡 214000; 3. 厦门大学附属中山医院创伤骨科,福建 厦门 361004 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金面上项目(51475397);厦门市科技计划项目(3502Z20173024);厦门市科技惠民项目(3502Z20154017) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 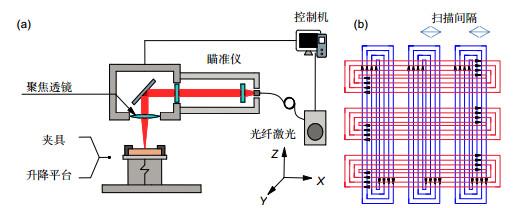
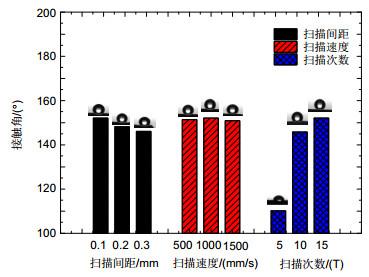
为开发出高性能生物医用干式电极,提出了利用激光微铣-重铸加工方法,实现了表面具有微结构阵列特征的新型金属干式电极的制造成形。在分析电极表面微观形貌的基础上,研究了电极表面的润湿性能,并重点研究了扫描间距、扫描速度和扫描次数等加工参数对大肠杆菌粘附性能的影响规律。研究结果表明:在一定工艺参数条件下所加工出具有微结构阵列特征的电极的接触角可达150°以上,表现出超疏水的特性。
在不同扫描间隙和扫描次数条件下加工出的电极对大肠杆菌的粘附性能具有较大影响,在选择0.1 mm扫描间隙时,电极表面粘附的大肠杆菌数量最少,适当增加扫描次数,也能够有效地减少电极表面大肠杆菌的粘结,从而发挥较好的抗菌效果。通过改变扫描速度加工出的电极则对大肠杆菌的粘附性能影响不大。
|
| 关 键 词: | 金属干式电极 表面微结构 粘附性能 润湿性 |
| 收稿时间: | 2017-08-08 |
| 修稿时间: | 2017-11-23 |
|
| 点击此处可从《光电工程》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《光电工程》下载全文 |
|



