| 地质体中天然氢气成因识别方法初探 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 孟庆强. 地质体中天然氢气成因识别方法初探[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(3): 552-558. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202203552 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 孟庆强 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.页岩油气富集机理与有效开发国家重点实验室, 北京 102206;;2.中国石化 石油勘探开发研究院, 北京 102206 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家重点研发计划项目(2017YFC0603102)和国家自然科学基金项目(41872164)联合资助。 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 
氢气作为一种清洁能源,已得到国内外越来越多的重视。近年我国加快氢能经济建设,对氢气的生产与储存提出了较高的要求。目前氢气的主要获取方式为人工制取氢气。了解自然界中是否存在高含量氢气,其成因如何,是能否发现并利用天然氢气的前提所在,但能否持续获得天然氢气,目前研究较弱。对氢气成因的判别,特别是深源成因与浅源成因主要依靠伴生稀有气体同位素组成特征进行判断,而部分天然气难以测定稀有气体,给氢气成因识别带来了困难。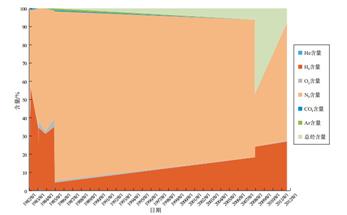
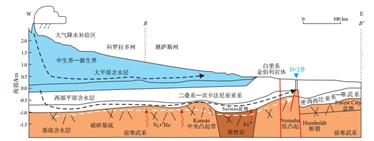
基于不同构造部位氢气及伴生气的含量、同位素组成等分析测试结果,分析美国堪萨斯(Kansas)盆地高含量氢气的持续时间和含量变化特征。并提出了基于甲烷—氢气含量关系与氢气氢同位素组成的氢气成因判别方法,降低了氢气成因识别的难度。认为地下条件下存在氢气补充机制,可以持续获得高含量天然氢气,板块碰撞带周边是高含量氢气的有利分布区。可以以氢气的氢同位素组成-700‰(VSMOW)和ln (CH4/H2)值划分氢气来源:壳源氢气的δD值一般大于-700‰,而ln (CH4/H2)值小于-8;幔源氢气的δD值一般小于-700‰,而ln (CH4/H2)值大于-4;富CO2流体在地表被氧化后剩余的氢气,其δD值大于-700‰,而ln (CH4/H2)值大于-8;深源富氢流体在地表被氧化后,剩余氢气的δD值小于-700‰,而ln (CH4/H2)值小于-4。该方法可以在不测定稀有气体组分及同位素组成的条件下,对氢气成因进行快速分类。
|
| 关 键 词: | 地质体 氢气 成因 识别方法 |
| 收稿时间: | 2022-01-12 |
| 修稿时间: | 2022-04-28 |
|
| 点击此处可从《石油实验地质》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《石油实验地质》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



