
|
|||||
|
|
| Al/Mo-C中间层对锆合金表面Zr2Al3C4涂层界面性能影响 | |
| 作者姓名: | 叶文浩 魏强 梁佳敏 周洁 孟凡平 EKLUND Per 黄庆 |
| 作者单位: | 1.天津大学 材料科学与工程学院, 天津 300350 2.中国科学院 宁波材料技术与工程研究所, 新能源技术研究所,宁波 315201 3.河北工业大学 机械工程学院, 天津 300130 4.Department of Physics, Chemistry, and Biology (IFM), Linköping University, Linköping 581 83, Sweden |
| 摘 要: | 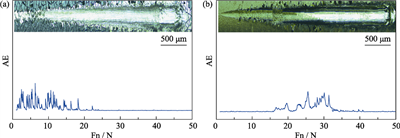 锆合金表面涂层研究作为提高核燃料包壳事故容错能力的重要技术手段之一, 能够有效解决失水事故下锆水反应的问题。Zr2Al3C4以其优异的抗氧化性能和适用于核环境的化学组分而成为锆合金包壳的候选涂层材料之一。由于Zr2Al3C4涂层与锆合金基底之间的元素扩散以及热膨胀系数不匹配等问题, 在其上制备Zr2Al3C4涂层的相关研究较少。本研究通过磁控溅射结合后续热处理工艺, 以Al/Mo-C作为扩散屏障层, 在锆合金基底上制备Zr2Al3C4涂层。结合X射线衍射仪、扫描电子显微镜和透射电子显微镜等分析手段, 研究了Al/Mo-C中间层对涂层的相和微观结构的影响。结果表明, 在800 ℃退火3 h后, 未添加中间层的涂层开裂, 同时由于Zr-Al-C涂层与基底之间存在明显的元素扩散, 导致Zr2Al3C4无法成相。Al/Mo-C中间层作为扩散屏障, 能够有效阻止退火过程中Zr-Al-C涂层和基底之间的元素扩散, 从而大大降低Zr-Al-C涂层与标准化学量比的偏差, 有利于最终涂层中Zr2Al3C4相的形成。此外, 该扩散屏障层能够抑制Zr2Al3C4涂层在退火过程中产生裂纹, 同时将退火态涂层与锆合金基底的结合力提高30 N。  |
| 关 键 词: | Zr2Al3C4 中间层 扩散屏障 结合力 |
| 收稿时间: | 2020-05-25 |
| 修稿时间: | 2020-08-20 |
| 点击此处可从《无机材料学报》浏览原始摘要信息 | |
| 点击此处可从《无机材料学报》下载全文 | |