Experimental measurement and correlation for solubility of piroxicam (a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)) in supercritical carbon dioxide |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Hamburg University of Technology, Institute of Thermal Separation Processes, Eissendorfer Str. 38, Hamburg 20173, Germany;2. Mendeleev University of Chemical Technology, International Science and Education Centre for Transfer of Biopharmaceutical Technologies, Geroev Panphilovtcev str. 20/1, Moscow 125480, Russian Federation |
| |
| Abstract: | 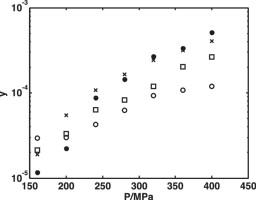
Since the knowledge of pharmaceutical solubilities in the supercritical carbon dioxide is one of the first essential necessities for designing the supercritical carbon dioxide-based processes, solubility of piroxicam a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug was experimentally measured. In this regard, a static method coupled with gravimetric method was used to measure the solubility of piroxicam in the supercritical carbon dioxide in temperature and pressure range of 308.15–338.15 K and 16–40 MPa, respectively. The obtained solubility data were in the range of 1.17 × 10−5 and 5.12 × 10−4 based on the mole fraction (mole piroxicam/(mole piroxicam + mole CO2)) then modeled using four different density based correlations namely Bartle et al., Mendez-Santiago-Teja, Chrastil and Kumar and Johnston models. The results of error analysis revealed that the used correlations were potential to correlate the solubility of piroxicam with minimum and maximum average absolute relative deviation percents (AARD%) of 14.4% and 15.2%, respectively. |
| |
| Keywords: | Solubility Supercritical carbon dioxide Piroxicam Correlation Extrapolation Semi-empirical correlations |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

